Windows 10 provides an inbuilt tool like a Control panel to help its users make changes to appearance and personalization, uninstall programs, and many more.
The control panel can sometimes become a problem for newbie users of computers to find. If you are one, worry no more!
This article will walk you through how to find control panel in Windows 10.
Things To Know
- To easily access the control panel in Windows, open the start menu and search Control menu then open it from there.
- Also, You can use the keyboard shortcut to open.
This article will walk you through two ways to open your control panel in Windows 10.
Using the Start Menu to Open Control panel
The start menu is the easiest and fastest method to use to open the control panel.
Simply follow these steps;
- Click Type here to search closer to the Start menu
- Type in Control Panel
- Then Click on Open
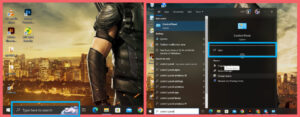
After pressing the Open, the control panel will open automatically.
Using the Keyboard Shortcut key to Open the Control panel
Alternatively, you can use the keyboard shortcut keys to open the run search box and run the control panel from there.
Follow these steps to open the control panel using keyboard shortcuts
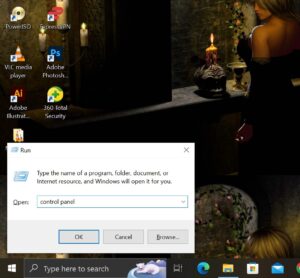
- Use the keyboard shortcut Windows key + R,
- Type control panel and press Enter
You can also check out our guide on Best Low End Pc/Laptops Games
The Control Panel provides a centralized hub for managing nearly every aspect of a Windows system, making it essential for both regular users and IT administrators to troubleshoot and maintain optimal performance.
1. System Settings Management
The Control Panel allows users to customize and control various aspects of the operating system, including:
- Display Settings: Change screen resolution, adjust brightness, or set up multiple monitors.
- Sound Settings: Configure input/output devices, adjust volume, and change audio enhancements.
- Network and Internet: Manage Wi-Fi, Ethernet, VPN, and network adapters.
2. User Accounts and Security
- User Management: Add, modify, or delete user accounts.
- Parental Controls: Set time limits and content restrictions for children’s accounts.
- Security and Maintenance: Access firewall settings, Windows Defender, and security reports.
3. Software Management
- Uninstall Programs: Remove or modify installed software.
- Default Programs: Choose default apps for certain tasks (like browsers or media players).
4. Hardware Configuration
- Device Manager: Install and update drivers for hardware devices.
- Printers and Scanners: Add and configure printers, scanners, and other devices.
5. System Maintenance and Performance
- Power Options: Customize power plans and sleep settings to optimize battery life.
- Backup and Restore: Create system backups and restore points.
- Date and Time Settings: Set regional time zones and clock configurations.
6. Accessibility Options
- Adjust settings for visually or hearing-impaired users (like Magnifier, Narrator, or On-Screen Keyboard).

